Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ariyoshi, Gen; Saruta, Koichi; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Maeno, Koki*; Li, Y.*; Tsutsui, Kihei*
Proceedings of 20th International Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal Hydraulics (NURETH-20) (Internet), p.1407 - 1420, 2023/08
Cavitation damage on a target vessel due to proton beam-induced pressure waves is one of the crucial issues for the pulsed neutron source using a mercury spallation target. As a mitigation technique for the damage, the helium microbubble injection into the mercury has been carried out by using a swirl bubbler in order to utilize compressibility of bubbles. Moreover, double-walled structure, which consists of an outer wall and an inner wall, has been applied as the target head structure. In this study, we aim to develop an abnormality diagnostic technology to detect the inner wall cracking, which is caused by such cavitation damage, from the outside of the target vessel. The mercury flow fields in the case with the cracking are evaluated by computational fluid dynamics analysis based on finite element method. And then, effect of the cracking on the flow field is discussed from the point of view of the flow-induced vibration and the acoustic vibration.
Wang, Z.; Iwasawa, Yuzuru; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki
Proceedings of 2020 International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE 2020) (Internet), 12 Pages, 2020/08
Ono, Ayako; Suzuki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 26th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-26) (Internet), 6 Pages, 2018/07
The mechanism of critical heat flux (CHF) for higher system pressure remains to be clarified, even though it is important to evaluate the CHF for the light water reactor (LWR) which is operated under the high pressure condition. In this study, the process of bubble coalescence was simulated by using a computational multi-fluid dynamics (CMFD) simulation code TPFIT under various system pressure in order to investigate the behavior of bubbles as a basic study. The growth of bubbles was simulated by blowing of vapor from a tiny orifice simulating bubble bottom. One or four orifices were located on the bottom surface in this simulation study. The numerical simulations were conducted by varying the pressure and temperature.
Koppitz, T.*; Jung, P.*; M ller, G.*; Weisenburger, A.*; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Ikeda, Yujiro
ller, G.*; Weisenburger, A.*; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Ikeda, Yujiro
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 343(1-3), p.92 - 100, 2005/08
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:44.84(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Cavitation damage of structural materials due to pressure waves is expected to be one of the majior life-time limiting factors in high power liquid metal spallation targets under pulsed operation. Two methods are developed for the European Spallation Source (ESS) to mitigate this damage: Introduction of gas bubbles to surpress the pressure pulse and surface-hardening of structural materials. Surface-hardening of four 8-13%Cr martenstic steels was examined by thermal treatment with pulsed or scanned electron- and laser-beams as well as by nitriding in plasma. A specimens of the 12%Cr steel were tested in liquid mercury under pulsed proton irradiation, and under mechanical pulsed-loading. Surface damage was analysed by optical, confocal-laser, or scanning-electron microscopy, showing in both tests much better resistance of the hardened material compared to standard condition.
 ) by laser ablation in superfluid helium at 1.5K
) by laser ablation in superfluid helium at 1.5KAratono, Yasuyuki; Wada, Akira*; Akiyama, Kazuhiko; Kitazawa, Shinichi; Hojo, Kiichi; Naramoto, Hiroshi*
Chemical Physics Letters, 408(4-6), p.247 - 251, 2005/06
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:2.99(Chemistry, Physical)C fulleren was detected in the deposit produced by the laser ablation in superfluid helium at 1.5K. From the mass spectrometry, it was found that the ratio,
fulleren was detected in the deposit produced by the laser ablation in superfluid helium at 1.5K. From the mass spectrometry, it was found that the ratio,  C
C /
/ C
C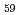
 C, differs from statistical one calculated by Poisson distribution for natural graphite. Assuming the recombination of atomic carbons to C
C, differs from statistical one calculated by Poisson distribution for natural graphite. Assuming the recombination of atomic carbons to C molecules as an initial stage for C
molecules as an initial stage for C formation, the different isotopic ratio of C
formation, the different isotopic ratio of C from Poisson statistics was ascribed to the tunneling recombination between
from Poisson statistics was ascribed to the tunneling recombination between  C and
C and  C atoms in the bubble state.
C atoms in the bubble state.
Ishikura, Shuichi*; Kogawa, Hiroyuki; Futakawa, Masatoshi; Kikuchi, Kenji; Hino, Ryutaro; Arakawa, Chuichi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 318, p.113 - 121, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:62.16(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal shock stress in the mercury target vessel was analyzed: the target receives the incident proton beam at the energy of 1 MW with the pulse duration of 1ms. Negative pressure of maximal 61MPa was generated when the initial pressure of 52MPa propagated in mercury. It is expected then that the cavitation may be arisen by the negative pressure. So in order to know the cavitation behavior, the simulation study was carried out by using the equation of motion based on the bubble dynamics for a single bubble, and fundamental parameter analysis was carried out. It is found that a bubble has a potential expansion more than 1000 times with a change of the pressure at the window of the target vessel. Consequently wave propagation will be affected. Theoretical consideration was given to the wave motion of propagation in bubbly liquid. The equation of state in bubbly liquid can be approximated by the polynomial. The diameter of a bubble and the bubble volume fraction inherent in mercury can be decided if the critical pressure, the sound velocity, and resonance frequency is successfully measured by static and dynamic experiment.
 HT and T+T
HT and T+T T
T in
in  He-
He- He quantum media under saturated vapor pressure at 1.6 K
He quantum media under saturated vapor pressure at 1.6 KAratono, Yasuyuki; Iguchi, Kazunari; Okuno, Kenji*; Kumada, Takayuki
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 107(19), p.3741 - 3746, 2003/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:11.71(Chemistry, Physical)An influence of superfluidity on recombination reactions of H+T HT, T+T
HT, T+T T
T in
in  He-
He- He quantum media was studied under saturated vapor pressure at 1.6 K. A change of reaction mechanism was observed at transition point from normalfluid to superfluid phase. Tunneling reaction mechanism by H and T bubble atoms was proposed on the basis of large isotope effect.
He quantum media was studied under saturated vapor pressure at 1.6 K. A change of reaction mechanism was observed at transition point from normalfluid to superfluid phase. Tunneling reaction mechanism by H and T bubble atoms was proposed on the basis of large isotope effect.
Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Nariai, Hideki*; Inasaka, Fujio*
JSME International Journal, Series B, 44(1), p.81 - 89, 2001/01
no abstracts in English
 -ZrO
-ZrO (Y){or ThO
(Y){or ThO }-Al
}-Al O
O -MgO at burn-up of 20 MWd/kg
-MgO at burn-up of 20 MWd/kgYanagisawa, Kazuaki; Omichi, Toshihiko; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki; Amano, Hidetoshi; Yamahara, Takeshi
JAERI-Research 97-085, 31 Pages, 1997/11
no abstracts in English
 Cu
Cu O
O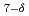 during He-ion irradiation in an electron microscope
during He-ion irradiation in an electron microscopeMaeta, Hiroshi; Furuno, Shigemi; Hojo, Kiichi; ; Watanabe, Mitsuo
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 179-181, p.1003 - 1006, 1991/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
; ; ; *; *
JAERI-M 86-087, 24 Pages, 1986/06
no abstracts in English
R.S.Kensley*; ; ; ; ; L.Dresner*; ;
JAERI-M 82-107, 15 Pages, 1982/08
no abstracts in English
Serizawa, Hiroyuki
no journal, ,
My investigation on cavities in ceramics was triggered by the unexpected discovery of a polyhedral cavity in a UO matrix. In a series of experiments, I noticed that the shape of the negative crystal changes depending on the heat-treatment history. In general, it is difficult to control arbitrarily the shapes of these polyhedral negative crystals embedded in a solid medium; however, the shape can easily be controlled using the helium injection method. Our research team named the shape controlled negative crystal as image crystal.
matrix. In a series of experiments, I noticed that the shape of the negative crystal changes depending on the heat-treatment history. In general, it is difficult to control arbitrarily the shapes of these polyhedral negative crystals embedded in a solid medium; however, the shape can easily be controlled using the helium injection method. Our research team named the shape controlled negative crystal as image crystal.